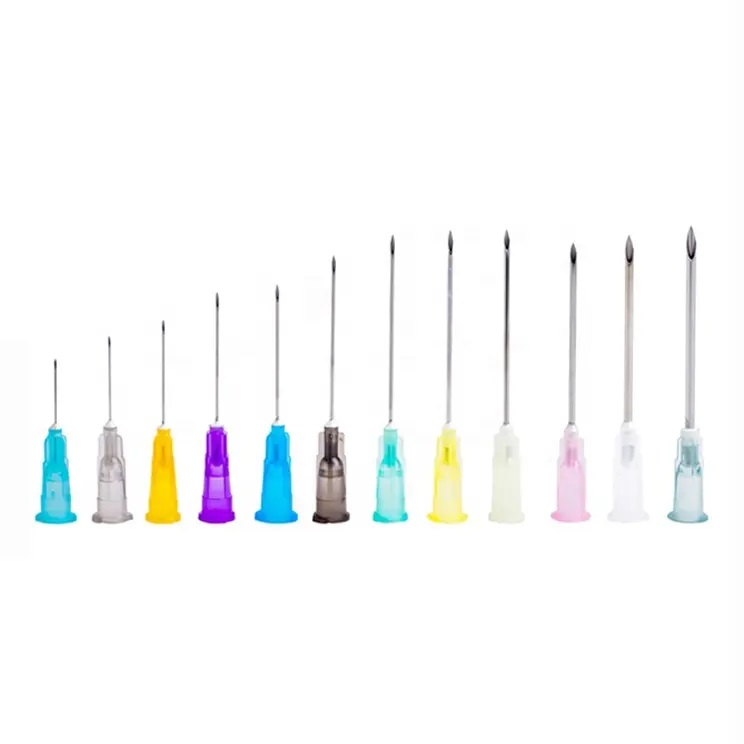
Disposable injection needle sizes measures in following two points:
Needle gauge: The higher the number, the thinner the needle.
Needle length: indicates the length of the needle in inches.
For example: A 22 G 1/2 needle has a gauge of 22 and a length of half an inch.
There are several factors which need to be considered in choosing the size of a needle to use for an injection or “shot”. They include such issues as:
How much medication you need.
Your body sizes.
Whether the drug has to go into a muscle or under the skin.
1. Quantity of the medication you need
For injecting a small amount of medication, you’d better to use a thin, high gauge needle. It will make you feel less painful than a wider, lower gauge needle.
If you need to inject a larger amount of medicine, a wider needle with a lower gauge is often a better choice. While it might hurt more, it will deliver the drug faster than a thin, high-gauge needle.
2. Your body sizes
Larger individuals may require longer and thicker needles to ensure that the medication reaches the intended target area. Conversely, smaller individuals may benefit from shorter and thinner needles to minimize discomfort and the potential for complications. Healthcare providers should take into account the patient’s body mass index and the specific injection site to determine the most suitable needle size for optimal results. Like people’s age, fat or thin, etc.
3. Whether the drug has to go into a muscle or under the skin.
Some medications can be absorbed just under the skin, while others need to be injected into the muscle:
Subcutaneous injections go into the fatty tissue just below the skin. These shots are fairly shallow. The needle required is small and short (typically one-half to five-eighths of an inch long) with a gauge of 25 to 30.
Intramuscular injections go directly into a muscle.4 Since muscle is deeper than the skin, the needle used for these shots has to be thicker and longer. Medical Needles with a gauge of 20 or 22 G and a length of 1 or 1.5 inches are usually best for intramuscular injections.
The following table outlines recommended needle gauges and lengths. In addition, clinical judgment should be used when selecting needles to administer injectable vaccines.
| Route | Age | Needle gauge and length | Injection site |
| Subcutaneous injection |
All ages | 23–25-gauge 5/8 inch (16 mm) |
Thigh for infants younger than 12 months of age; upper outer triceps area for persons 12 months of age and older |
| Intramuscular injection |
Neonate, 28 days and younger | 22–25-gauge 5/8 inch (16 mm) |
Vastus lateralis muscle of anterolateral thigh |
| Infants, 1–12 months | 22–25-gauge 1 inch (25 mm) |
Vastus lateralis muscle of anterolateral thigh |
|
| Toddlers, 1–2 years | 22–25-gauge 1–1.25 inches (25–32 mm) |
Vastus lateralis muscle of anterolateral thigh |
|
| 22–25-gauge 5/8–1 inch (16–25 mm) |
Deltoid muscle of arm | ||
| Children, 3–10 years | 22–25-gauge 5/8–1 inch (16–25 mm) |
Deltoid muscle of arm | |
| 22–25-gauge 1–1.25 inches (25–32 mm) |
Vastus lateralis muscle of anterolateral thigh |
||
| Children, 11–18 years | 22–25-gauge 5/8–1 inch (16–25 mm) |
Deltoid muscle of arm | |
| Adults, 19 years and older 130 lbs (60 kg) or less 130–152 lbs (60–70 kg) Men, 152–260 lbs (70–118 kg) Women, 152–200 lbs (70–90 kg) Men, 260 lbs (118 kg) or more Women, 200 lbs (90 kg) or more |
22–25-gauge 1 inch (25 mm) 1 inch (25 mm) 1–1.5 inches (25–38 mm) 1–1.5 inches (25–38 mm) 1.5 inches (38 mm) 1.5 inches (38 mm) |
Deltoid muscle of arm |
Our Company Shanghai Teamstand Corporation is one of the leading manufacturers of IV sets, syringes, and medical needle for syringe , huber needle, blood collection set, av fistula needle, and so on. Quality is our highest priority, and our quality assurance system is certified and meets the standards of the Chinese National Medical Products Administration, ISO 13485, and the European Union’s CE mark, and some passed FDA approval.
Please contact us freely for more information.
Post time: Apr-08-2024