Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition where a blood clot forms in the deep veins, most commonly in the legs. These clots can block blood flow and lead to complications such as pain, swelling, and redness. In severe cases, a clot may dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing a potentially life-threatening condition known as a pulmonary embolism (PE). Addressing DVT promptly is critical to prevent these complications and maintain healthy blood flow.
What Causes DVT?
DVT typically arises from factors that impede normal blood flow or increase the blood’s tendency to clot. These factors include prolonged immobility (such as during long flights or hospital stays), injury to a blood vessel, surgery, and certain medical conditions like cancer or clotting disorders. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle, also contribute to the risk of developing DVT.
Treatment Options for DVT
Treatment for DVT focuses on preventing clot growth, reducing symptoms, and minimizing the risk of complications. Common approaches include:
- Anticoagulant Medications: Blood thinners, such as warfarin or newer oral anticoagulants, help prevent clot formation and allow existing clots to dissolve over time.
- Compression Stockings: These specialized stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, promoting blood flow and reducing swelling.
- Physical Activity: Gradual movement and exercises recommended by a healthcare provider help maintain circulation and reduce clot risk.
- DVT Pumps: DVT pumps are mechanical devices designed to improve blood flow in the veins and are especially useful for individuals at high risk of DVT due to immobility or surgery.
DVT Pumps: Enhancing Blood Flow in the Veins
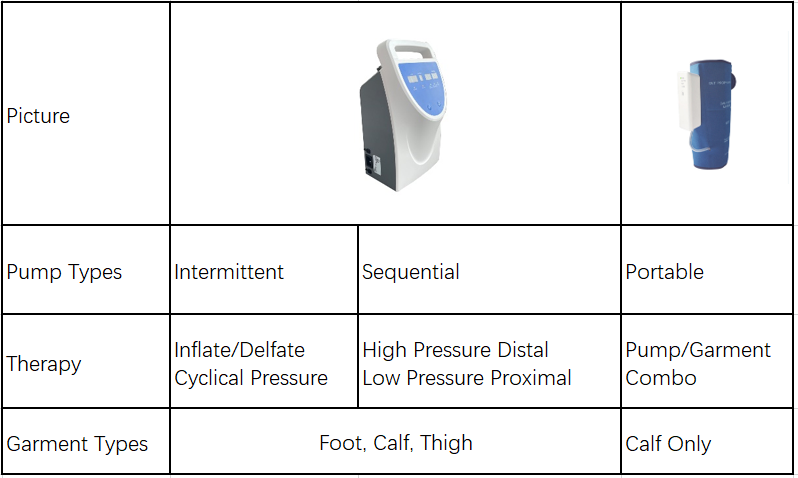
DVT pumps are a critical tool in preventing and managing DVT. These devices work by mimicking the natural pumping action of the calf muscles, encouraging blood flow through the deep veins and reducing the risk of clot formation. Here, we discuss three main types of DVT pumps: intermittent pumps, sequential pumps, and portable pumps.
1. Intermittent Pumps
Intermittent pumps deliver pulsating pressure to the affected limb. These devices inflate and deflate periodically, mimicking the body’s natural blood-pumping action. The intermittent compression reduces blood stasis (pooling) and promotes efficient blood flow through the veins. These pumps are often used in hospital settings for patients recovering from surgery or those confined to bed for extended periods.
Advantages:
- Simple and effective mechanism.
- Ideal for stationary patients in clinical environments.
Limitations:
- Limited mobility as these pumps are typically bulky.
- Requires a power source.
2. Sequential Pumps
Sequential pumps provide graduated compression by inflating different chambers of the device in a sequential manner, starting from the ankle and moving upward toward the thigh. This pattern simulates the natural flow of blood through the veins, further enhancing circulation and reducing the risk of clot formation.
Advantages:
- Offers targeted and comprehensive compression.
- Particularly effective for patients with more severe circulation issues.
Limitations:
- Can be more expensive than intermittent pumps.
- Requires professional guidance for optimal use.
3. Portable Pumps
Portable DVT pumps are lightweight, battery-operated devices designed for convenience and mobility. These pumps are ideal for patients who need DVT prevention while traveling or during daily activities. Despite their compact size, portable pumps provide effective compression and are easy to use.
Advantages:
- Highly convenient and versatile.
- Encourages patient compliance due to ease of use.
Limitations:
- May have less powerful compression compared to clinical-grade devices.
- Battery life needs monitoring and frequent recharging.
Choosing the Right DVT Pump
The choice of a DVT pump depends on the patient’s specific needs, lifestyle, and medical condition. Intermittent pumps are suitable for stationary use in hospitals, sequential pumps are ideal for targeted therapy, and portable pumps cater to active individuals who require mobility. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the most appropriate option.
The Importance of DVT Pump Maintenance
Proper maintenance of a DVT pump is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and longevity. Regular cleaning, checking for wear and tear, and following the manufacturer’s instructions are essential practices. Patients and caregivers should also ensure that the device is correctly fitted and functioning as intended to maximize therapeutic benefits.
Conclusion
DVT pumps play an indispensable role in the prevention and management of deep vein thrombosis. By enhancing blood flow and reducing the risk of clot formation, these devices offer a lifeline to patients at risk of this serious condition. Understanding the differences between intermittent, sequential, and portable pumps helps patients and caregivers make informed decisions tailored to their needs. With the right DVT pump and proper usage, individuals can significantly improve their vascular health and overall quality of life.
Post time: Dec-23-2024