Central venous catheters (CVCs) and peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs) are essential tools in modern medicine, used to deliver medications, nutrients, and other essential substances directly into the bloodstream. Shanghai Teamstand Corporation, a professional supplier and manufacturer of medical devices, provides both types of catheters. Understanding the differences between these two types of catheters can help healthcare professionals choose the right device for their patients.
What is a CVC?
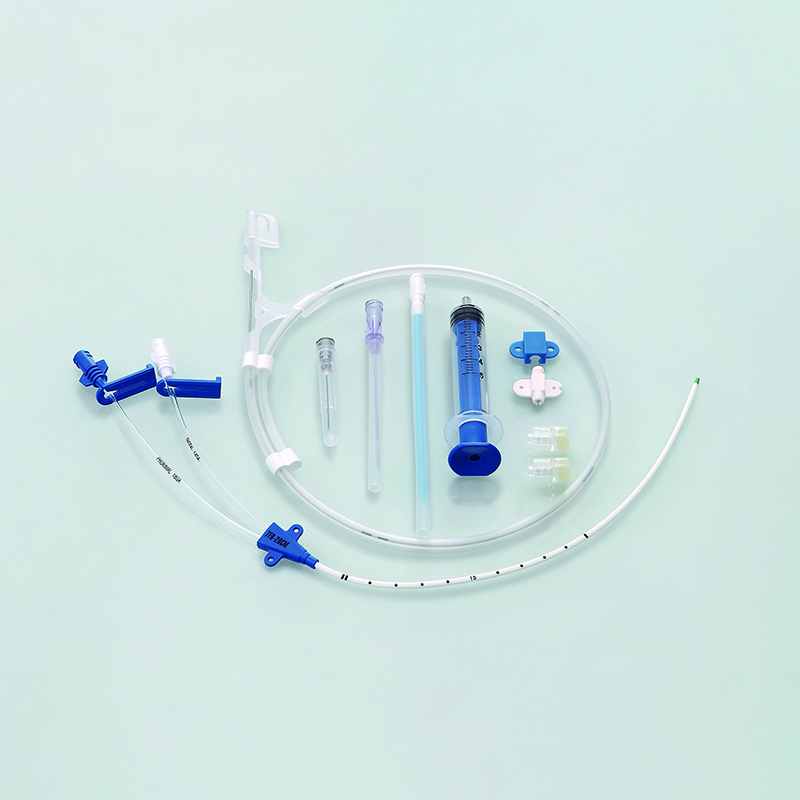
A Central Venous Catheter (CVC), also known as a central line, is a long, thin, flexible tube inserted through a vein in the neck, chest, or groin and advanced into the central veins near the heart. CVCs are used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Administering medications: Especially those that are irritating to peripheral veins.
– Providing long-term intravenous (IV) therapy: Such as chemotherapy, antibiotic therapy, and total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
– Monitoring central venous pressure: For critically ill patients.
– Drawing blood for tests: When frequent sampling is required.
CVCs can have multiple lumens (channels) allowing for the simultaneous administration of different therapies. They are generally intended for short to medium-term use, typically up to several weeks, although some types can be used for longer periods.
What is a PICC?
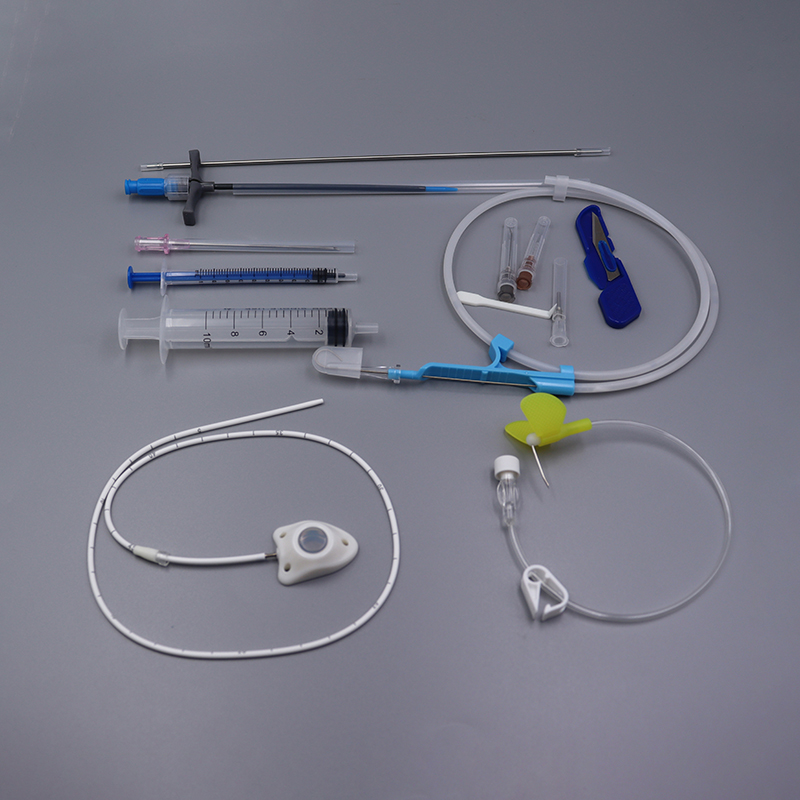
A Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) is a type of central catheter inserted through a peripheral vein, usually in the upper arm, and advanced until the tip reaches a large vein near the heart. PICCs are used for similar purposes as CVCs, including:
- Long-term IV access: Often for patients requiring extended therapy such as chemotherapy or long-term antibiotic treatment.
– Administering medications: That need to be delivered centrally but over a longer period.
– Drawing blood: Reducing the need for repeated needle sticks.
PICCs are typically used for longer durations than CVCs, often from several weeks to months. They are less invasive than CVCs as their insertion site is in a peripheral vein rather than a central one.
Key Differences Between CVC and PICC
1. Insertion Site:
– CVC: Inserted into a central vein, often in the neck, chest, or groin.
– PICC: Inserted into a peripheral vein in the arm.
2. Insertion Procedure:
– CVC: Typically inserted in a hospital setting, often under fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance. It usually requires more sterile conditions and is more complex.
– PICC: Can be inserted at the bedside or in an outpatient setting, usually under ultrasound guidance, making the procedure less complex and invasive.
3. Duration of Use:
– CVC: Generally intended for short to medium-term use (up to several weeks).
– PICC: Suitable for longer-term use (weeks to months).
4. Complications:
– CVC: Higher risk of complications such as infection, pneumothorax, and thrombosis due to the more central location of the catheter.
– PICC: Lower risk of some complications but still carries risks such as thrombosis, infection, and catheter occlusion.
5. Patient Comfort and Mobility:
– CVC: Can be less comfortable for patients due to the insertion site and potential for movement restriction.
– PICC: Generally more comfortable and allows greater mobility for patients.
Conclusion
Both CVCs and PICCs are valuable medical devices provided by Shanghai Teamstand Corporation, each serving specific needs based on the patient’s condition and treatment requirements. CVCs are typically chosen for short-term intensive treatments and monitoring, while PICCs are favored for long-term therapy and patient comfort. Understanding these differences is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions and provide the best care for their patients.
Post time: Jul-08-2024